Legal aid, as we know it today, is a relatively recent institutional development, but the concept is old. From the Court of Requests in Tudor and early Stuart times to the pro bono advice offered by the Poor Man’s Lawyers Movement, the idea that everyone is entitled to some form of legal advice and support has been present in the United Kingdom for a long time.
However, legal aid as charity did little to help those unable to pay for legal counsel (it was, after all, mostly restricted to pre-trial advice) or to level the legal playing field, as the courts continued to be part of the modus vivendi of the aristocracy. Due to strong opposition to the idea that everyone should be entitled to legal aid (mainly for fear of encouraging people to be litigious), some of the first formal policies were, perhaps inevitably, heavily moralized. For example, the Poor Prisoners Defence Act 1903 included provisions for legal aid for prisoners who had a defence.
The end of World War II led to the foundation of legal aid roughly as we know it today. Since then, several reforms have attempted to manage both the volume and the cost of legal aid, with the post-1986 cuts being the first concentrated effort to reduce the budget. In April 2013, the Legal Aid, Sentencing and Punishment of Offenders Act 2012 (LASPO) introduced further cuts, which heavily affected several areas of litigation and excluded most private family law cases from the scope of legal aid.
LASPO and the Right to Legal Aid
LASPO’s explicit goal was to save money and family law was one of its main targets. While public law proceedings and the representation of children generally remained in scope, private family law was the reform’s main ‘victim’. Most private family law cases, including procedures as common and stressful as divorce and child contact, became ineligible for legal aid. Cases involving children or finance remain in scope only where there are issues concerning domestic violence or child abuse and specific evidence is provided (the evidence-related requirements relaxed in 2018). The Ministry of Justice expected that this new policy would also discourage litigation on private family problems, which could be resolved out of court. Apparently, the idea that people become unreasonably or excessively litigious if legal support is readily available still survives.
One possible concern with this blanket approach is that the exclusion of entire areas of law seems arbitrary and irreconcilable with the very raison d’ être of legal aid. Even where alternative means of dispute resolution (such as mediation) are available, some of these cases may inevitably end up in court. Furthermore, mediation itself requires legal support and, as we will see, there is evidence that people need to be advised by a lawyer that it is an available option. The problem, therefore, with the removal of almost the entire area of private family law from civil legal aid is that this policy choice may restrict access to justice for many people, without consideration for their needs and circumstances.
The idea that access to civil legal aid is inherently linked with effective access to justice is part of the European legal tradition. Article 47 of the European Charter of Fundamental Rights 2000 illustrates the point: ‘Legal aid shall be made available to those who lack sufficient resources in so far as such aid is necessary to ensure effective access to justice.’ However, there is no universal or unconditional right to legal aid, especially with regard to civil law cases. While efficient access to justice remains important for the European Court of Human Rights (‘the Court’), it has been ruled that Article 6 § 1 does not imply that the State must provide free legal aid for every dispute relating to a ‘civil right’ (Airey v. Ireland, § 26). The crucial question is whether the lack of legal aid would deprive the applicant of a fair hearing and the answer depends on the specific circumstances of the case (Airey v. Ireland, § 26; Steel and Morris v. the United Kingdom, § 61; McVicar v. the United Kingdom, § 48).
The Court has identified a set of criteria for assessing the states’ obligation to make legal aid available in non-criminal proceedings. These are: the importance of what is at stake for the applicant (Steel and Morris v. the United Kingdom, § 61; P., C. and S. v. the United Kingdom, § 100); the complexity of the relevant law or procedure (Airey v. Ireland, § 24); the applicant’s capacity to represent him/herself effectively (McVicar v. the United Kingdom, §§ 48-62; Steel and Morris v. the United Kingdom, § 61); and the existence of a statutory requirement to have legal representation (Airey v. Ireland, § 26; Gnahoré v. France, § 41). Two further criteria have emerged in the Court’s case law regarding the conditions attached to legal aid: the financial situation of the litigant; and the prospects of success in the proceedings (Steel and Morris v. the United Kingdom, § 62).
LASPO and access to justice: the project’s findings
The question that naturally emerges from these general remarks is whether LASPO was successful in saving money without ignoring the above criteria and restricting access to justice for many people who require legal aid to effectively exercise this right. In a research project funded by the British Academy, Theodoros Alysandratos, Mariol Jonuzaj and I looked at the effect of LASPO on family law cases, hoping to shed some light on these issues.
First, we find that legal aid funding started to drop in the first financial quarter of 2014 and kept on falling for the next two years. At the end of this period, funding had dropped by 35% relative to the amount approved before the fall started.
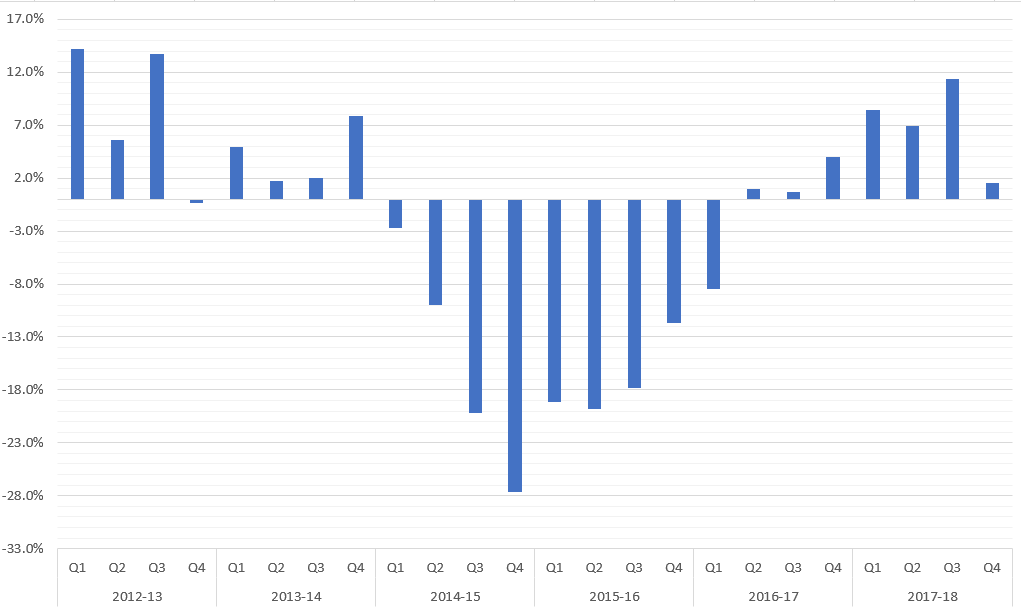
This graph shows the Legal Aid by Financial Year and Financial Quarter and is for illustration purposes. The data shows the percentage change of legail aid on a year-to-year basis.
Legal Aid by Financial Year and Financial Quarter. The image illustrates the percentage change on year-to-year basis.
Then, we observe that the number of funded cases started to drop in the first financial quarter of 2012 and continued for 3 years. At the end of this period about 60-65% fewer cases were being funded. The discrepancy in the timing of the effects between funding and funded cases can likely be attributed to the disbursement of commitments prior to LASPO coming into effect.
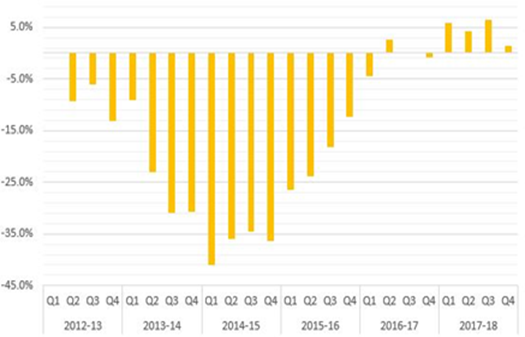
Volume by Financial Year and Financial Quarter. The image illustrates the percentage change on year-to-year basis.
Volume by Financial Year and Financial Quarter. The image illustrates the percentage change on year-to-year basis.
In terms of saving money, the case of private family law reveals that the LASPO had an immediate effect. Whether this effect was sustained in the years that followed remains to be seen. The same applies to the number of cases that received legal aid, since it also dropped significantly in the years immediately following LASPO. This means that, at least for a certain period of time, a considerable number of people was denied access to legal aid for private family law cases (with the exceptions noted in the introductory paragraph), regardless of their financial situation and/or ability to secure some kind of legal advice, let alone representation.
Did this lead to an increase in the number of cases going to mediation or the number of Mediation Information and Assessment Meetings (MIAMs)? According to the post-legislative memorandum released by the Ministry of Justice in 2017, this was certainly not the case, presumably because it is only after receiving legal advice that most people see mediation as an option. In fact, before LASPO came into force, 4 out of 5 cases that ended up in MIAMs were referrals from legally aided solicitors. To make things worse, the in 2017 that only 61% of completed mediations were successful (slightly down from the 68% reported for 2013-2014).
This evidence suggests that, as far as legal aid is concerned, many people in England and Wales are experiencing a return to a pre-World War II world. Their chances of securing free legal advice and representation are very slim, as their only avenue is to contact organisations with already limited resources, such as Citizens Advice and Family First. University Law Clinics also shoulder some of the burden, but they cannot offer legal representation. In a sense, civil legal aid is to an extent seen, once again after almost a century, as a form of charity.
However, as lawyers realised at the time, charity is not enough to ensure effective access to justice for all. As one of the founders of the Poor Man’s Lawyers Movement observed more than 120 years ago, extensive lack of free access to legal advice and representation for those who most need them makes the rule of law ‘an anaemic attenuated make-believe which we flash in the eyes of the poor as justice’.
First published on the Essex Law Research Blog.


